Rhinoplasty Surgeon Austin Fundamentals Explained
Table of ContentsThe Greatest Guide To Rhinoplasty Austin TxExamine This Report about Rhinoplasty Surgeon Austin8 Simple Techniques For Rhinoplasty Austin Tx
Based upon the readily available location of nasal skin, the cosmetic surgeon selects the place for the bilobed flap, and orients the pedicle. If the flaw remains in the lateral element of the nose, the pedicle is based medially. If the problem is at the nasal idea, or at the nasal dorsum, the pedicle is based laterally.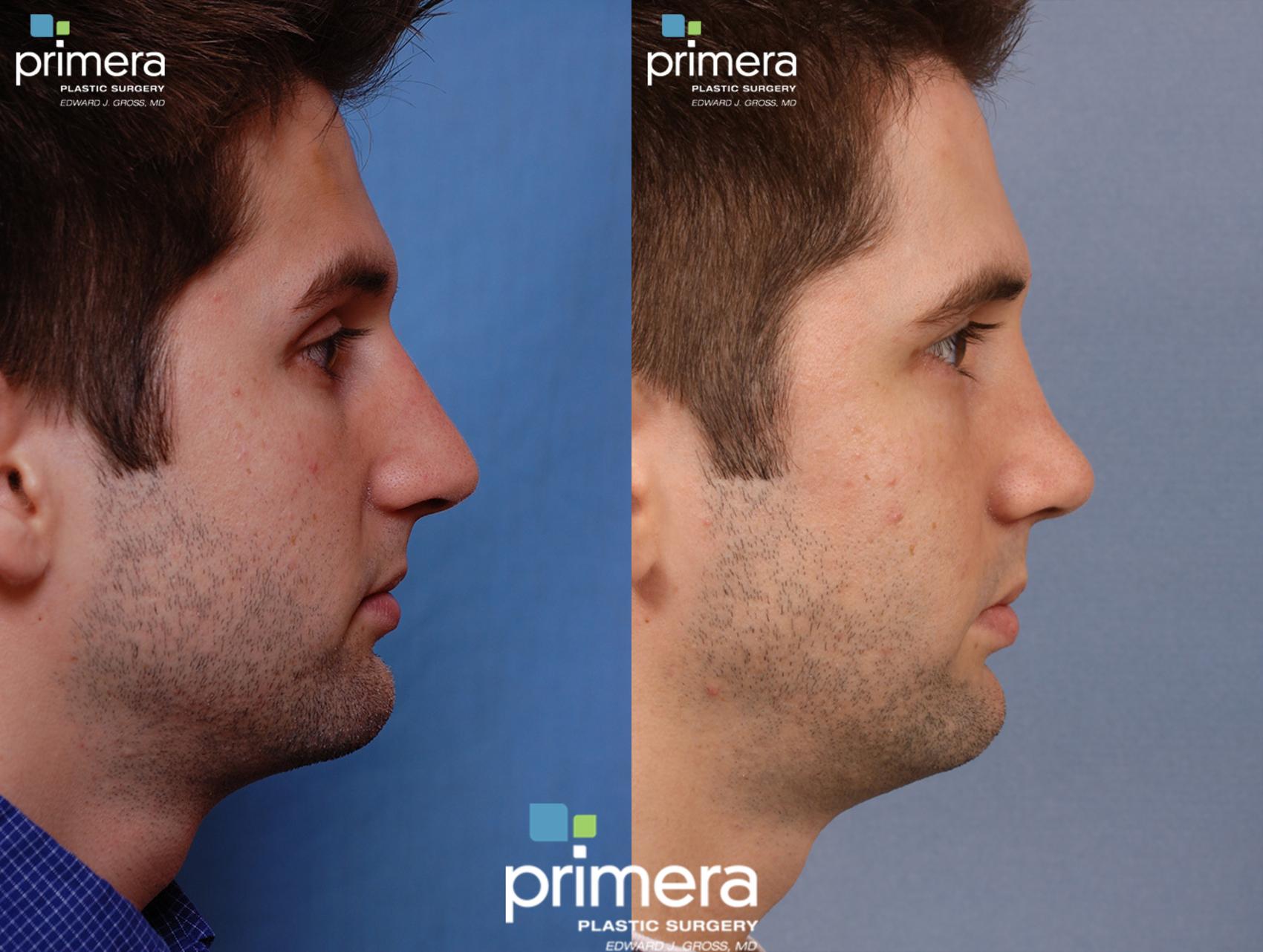

The outer semi-circle defines the necessary length of the two lobes of the skin flap. The inner semi-circle bisects the center of the initial wound, and continues throughout the donor skin, developing limit procedure of the pedicle common to the 2 lobes of the flap. The cosmetic surgeon then draws two lines from the peak of the injury; the first line drawn is at an angle of 45 degrees from the long axis of the wound, and the 2nd line drawn is at a 90-degree angle from the axis of the wound.
The delineation of each of the two lobes of the flap starts and ends at the inner semi-circle, and encompasses the external semi-circle, to the point where it converges its main axis. The width of the first lobe is roughly 2 mm narrower than the width of the injury; the width of the 2nd lobe is around 2 mm narrower than the width of the first lobe.
The injury is deepened, down to the nasal skeleton, to accommodate the tissue density of the bilobed flap (rhinoplasty surgeon austin). Technically, cutting the injury, expanding it, is more effective, and much safer, than cutting (thinning) the flap to fit the injury. Undermining the donor site for the 2nd lobe enables closing it mainly; it likewise eliminates excess-skin "dog-ears" at the donor site.
II. Nasolabial flap In the 19th century, the surgical methods of J.F. Dieffenbach (17921847) promoted the nasolabial flap for nasal restoration, for which it remains a fundamental nose surgery procedure. The nasolabial flap can be either superiorly based or inferiorly based; of which the superiorly based flap is the more useful rhinoplastic application, since it has a more versatile arc of rotation, and the donor-site scar is unnoticeable.
The Main Principles Of Rhinoplasty Surgeon Austin
The blood supply for the flap pedicle are the transverse branches of the contralateral angular artery (the facial artery terminus parallel to the nose), and by a confluence of capillary from the angular artery and from the supraorbital artery in the medial canthus, (the angles formed by the meeting of the upper and lower her response eyelids) (rhinoplasty austin tx).
The nasolabial flap is a random flap that is emplaced with the proximal (near) part resting upon the lateral wall of the nose, and the distal (far) portion resting upon the cheek, which includes the primary angular artery, therefore is perfused with retrograde arterial flow. Surgical method the nasolabial flap The pedicle of the nasolabial flap rests upon the lateral nasal wall, and is transposed an optimum of 60 degrees, in order to avoid the "bridge result" of a flap emplaced throughout the nasofacial angle.
The shape of the skin flap is cut from the injury template fabricated by the cosmetic surgeon. A cut is made to the flap (without an anaesthetic injection of epinephrine), which then is raised and oriented, in an inferior-to-superior direction, between the subcutaneous fat and the muscle fascia. The cutting continues up until the skin flap can be easily shifted upon the nasal problem.
The flap then is bent back (reflected), and can be thinned (cut) under loupe zoom; however, a nasolabial flap can not be thinned as easily as an axial skin-flap. austin rhinopasty surgeon. After the nasolabial flap has actually been emplaced, the flap donor-site wound is sutured closed. For a wound of the lateral address nasal wall that is less than 15 mm wide, the flap donor-site can be closed primarily, with stitches.

Such threats are avoided by advancing (moving) the skin of the cheek towards the nasofacial junction, where it is sutured to the deep tissues. Additionally, a narrow injury, less than 1 mm broad can be permitted to recover by secondary objective (autonomous re-epithelialisation). III. The paramedian forehead flap The paramedian forehead flap is the premier autologous skin graft for the restoration of a nose, by changing any of the visual nasal subunits, particularly relating to the issues of various tissue density and skin color.
Limited length is an useful application limit of the paramedian forehead flap, specifically when the patient has a low frontal hairline. In such a patient, a small portion of scalp skin can be consisted of to the flap, however it does have a different skin texture and does continue growing hair; such mismatching is avoided with the transverse emplacement of the flap along the hairline; yet that portion of the skin flap is random, and so risks a higher incidence of necrosis.
Unknown Facts About Austin Rhinopasty Surgeon
Nonetheless, the 2nd phase of the nasal reconstruction can be performed with the client under regional anaesthesia. Aesthetically, although the flap donor-site scar heals well, it is obvious, and hence hard to hide, particularly in males. Nose surgery: A paramedian forehead flap style. Surgical technique the paramedian forehead flap The cosmetic surgeon develops the paramedian helpful hints forehead flap from a custom-fabricated three-dimensional metal foil template originated from the procedures of the nasal defect to be corrected.
Later on, the distal half of the flap is dissected and thinned to the subdermal plexus. The surgeon makes a metal foil design template stemmed from the dimensions of the nasal wound. Using a Doppler ultrasonic scanner, the surgeon identifies the axial pedicle of the tissue-flap (made up of the supraorbital artery and the supratrochlear artery), typically at the base, beside the median brow; the point typically is in between the midline and the supraorbital notch.